BASIC FIRE FIGHTING SYSTEM LAYOUT
The block diagram of the hardware implementation of the fire system is shown in Figure (1). The aim of the design is to illustrate the usage of the firefighting system and its applications. The minimum equipment required to construct the firefighting system is a microcontroller, pump water, smoke sensor, temperature sensor, flame sensor, LED’s, GSM modem.
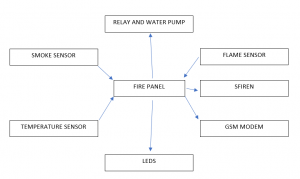
Smoke Sensor: A smoke detector is a device that detects smoke, typically as an indicator of fire. Commercial, industrial, and mass residential devices issue a signal to a fire alarm system, while household detectors, known as smoke alarms, generally issue a local audible or visual alarm from the detector itself. Smoke detectors are typically housed in a disk-shaped plastic enclosure Most smoke detectors work either by optical detection (photoelectric) or by physical process (ionization), while other use both detection methods to increase sensitivity to smoke. Sensitive alarms can be used to detect, and thus, smoking in areas where it is banned such as toilets and schools. Smoke detectors in large commercial, industrial, and residential buildings are usually powered by a central fire alarm system, which is powered by the building power with a battery backup.
LM35 Temperature Sensor: These sensors use a solid-state technique to determine the temperature. They use the fact as temperature increases, the voltage across a diode increases at a known rate. (Technically, this is the voltage drop between the base and emitter – the Vbe – of a transistor). By precisely amplifying the voltage change, it is easy to generate an analog signal that is directly proportional to temperature. There have been some improvements on the technique but, essentially that is how temperature is measured. Because these sensors have no moving parts, they are precise, never wear out, do not need calibration, work under many environmental conditions, and are consistent between sensors and readings. Moreover, they are easy to use.
Flame Sensor: This Flame Sensor can be used to detect fire source or other light sources of the wavelength in the range of 760nm – 1100 nm. It is based on the YG1006 sensor which is a high speed and highly sensitive NPN silicon phototransistor. Due to its black epoxy, the sensor is sensitive to infrared radiation.
Microcontroller: It is the heart of the system which controls all the activities of transmitting and receiving. A microcontroller (also MCU or µC) is a functional computer system-on-a chip. It contains a processor core, memory, and programmable input/output peripherals. Microcontrollers include an integrated CPU, memory (a small amount of RAM, program memory, or both) and peripherals capable of input and output. The IC used is ATmega 32. It is an 8-bit microcontroller with 32 Kbytes of In-System Programming Flash Memory. The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high-density non-volatile memory technology and is compatible with the industry standard 80C51 instruction set and pin out. The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be or programmed in-system or by a conventional non-volatile memory programmer. BASCOM_AVR programmers Notepad is used. The code after compilation generates ‘.hex’ file which is a hardware level code.
Relay: A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a witching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits).
Pump water: Pump is a device used to move fluids (liquids or gases) or sometimes slurries by mechanical action. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps. Pumps must have a mechanism which operates them and consume energy to perform mechanical work by moving the fluid. The activating mechanism is often reciprocating or rotary.
Light Emitting Diode (LED): A light-emitting diode (LED) is a two-lead semiconductor light source that resembles a basic pn-junction diode, except that an LED also emits light. When an LED’s anode lead has a voltage that is more positive than its cathode lead by at least the LED’s forward voltage drops, current flows. Electrons can recombine with holes within the device, releasing energy in the form of photons. This effect is called electroluminescence, and the colour of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photon) is determined by the energy band gap of the semiconductor.
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications): GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications), is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). GSM is used to send signal to fire fighter in case of fire.
Siren: It is used to generate alarm sound whenever any of the sensors become active.
For more information on Safety Training do click this link to MASMA Safety or click here for more information. Do not hesitate to call us at 019-2000643. MASMA Fire Engineering – Your Trusted Fire Contractor.
